(PDF) NeuroRDF: Semantic integration of highly curated data to prioritize biomarker candidates in Alzheimer's disease
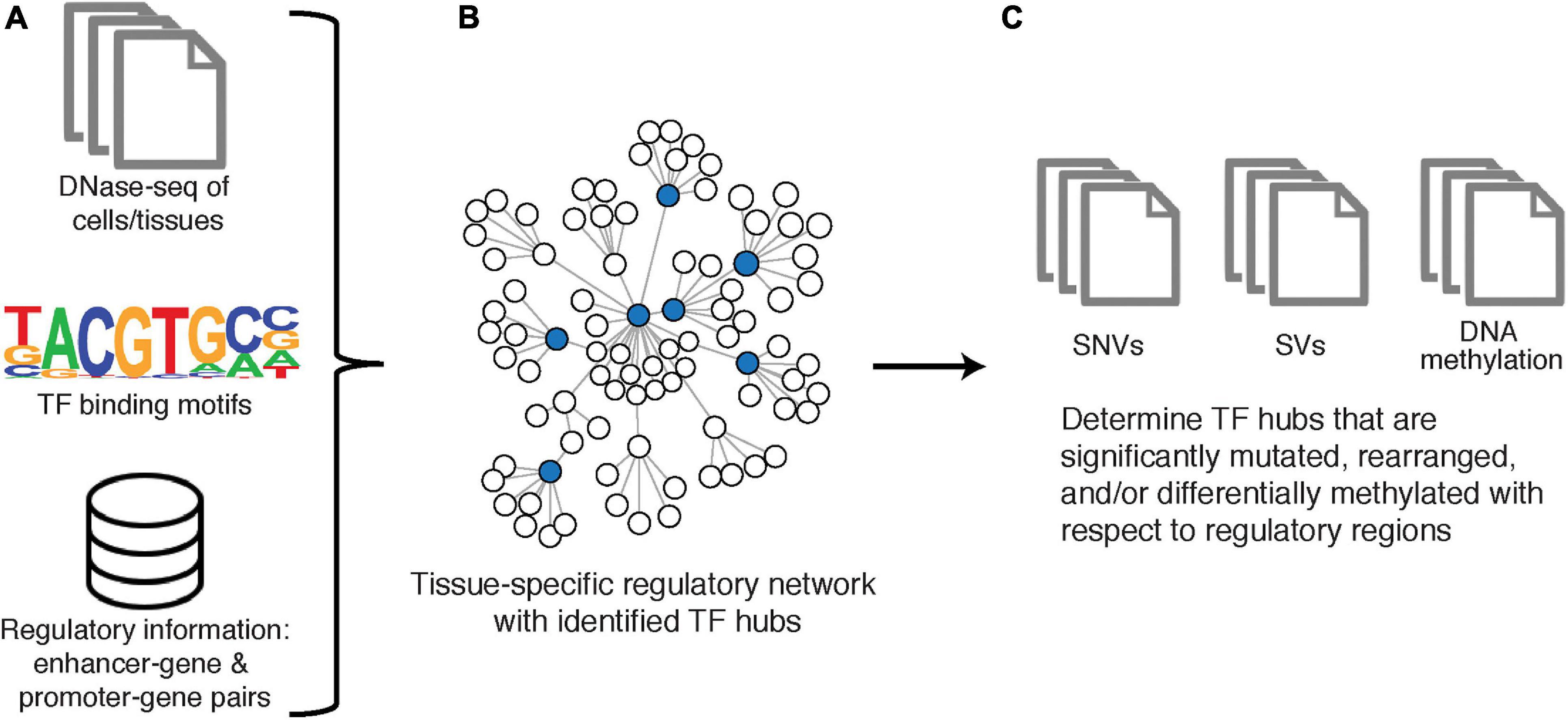
Frontiers | Mechanism-Centric Approaches for Biomarker Detection and Precision Therapeutics in Cancer
Full article: Application of Bayesian networks in determining nanoparticle-induced cellular outcomes using transcriptomics

Ractopamine at legal residue dosage accelerates atherosclerosis by inducing endothelial dysfunction and promoting macrophage foam cell formation - ScienceDirect

Ractopamine at legal residue dosage accelerates atherosclerosis by inducing endothelial dysfunction and promoting macrophage foam cell formation - ScienceDirect

Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression and Vulnerability to Rupture | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
Identification of potential drug targets for vascular dementia and carotid plaques by analyzing underlying molecular signatures

Ractopamine at legal residue dosage accelerates atherosclerosis by inducing endothelial dysfunction and promoting macrophage foam cell formation - ScienceDirect
nyc-schools-water-20160325/schools201516.csv at master · datanews/nyc-schools-water-20160325 · GitHub
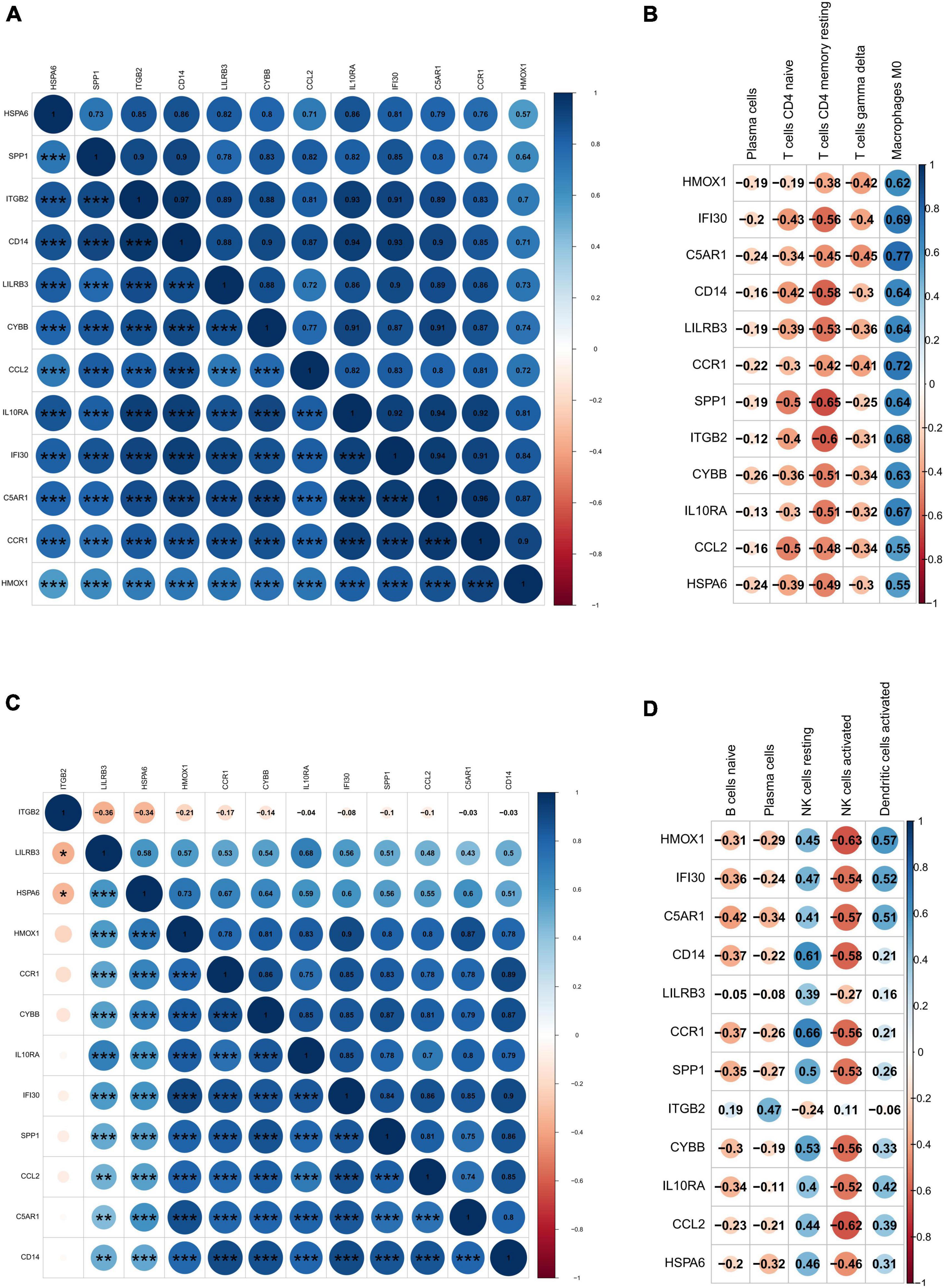
Frontiers | Identification of potential drug targets for vascular dementia and carotid plaques by analyzing underlying molecular signatures shared by them
Impact of C-reactive protein on osteo-/chondrogenic transdifferentiation and calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells | Aging
Identification of potential drug targets for vascular dementia and carotid plaques by analyzing underlying molecular signatures
Identification of potential drug targets for vascular dementia and carotid plaques by analyzing underlying molecular signatures
Identification of potential drug targets for vascular dementia and carotid plaques by analyzing underlying molecular signatures
Impact of C-reactive protein on osteo-/chondrogenic transdifferentiation and calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells | Aging
Impact of C-reactive protein on osteo-/chondrogenic transdifferentiation and calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells | Aging

Ractopamine at legal residue dosage accelerates atherosclerosis by inducing endothelial dysfunction and promoting macrophage foam cell formation - ScienceDirect
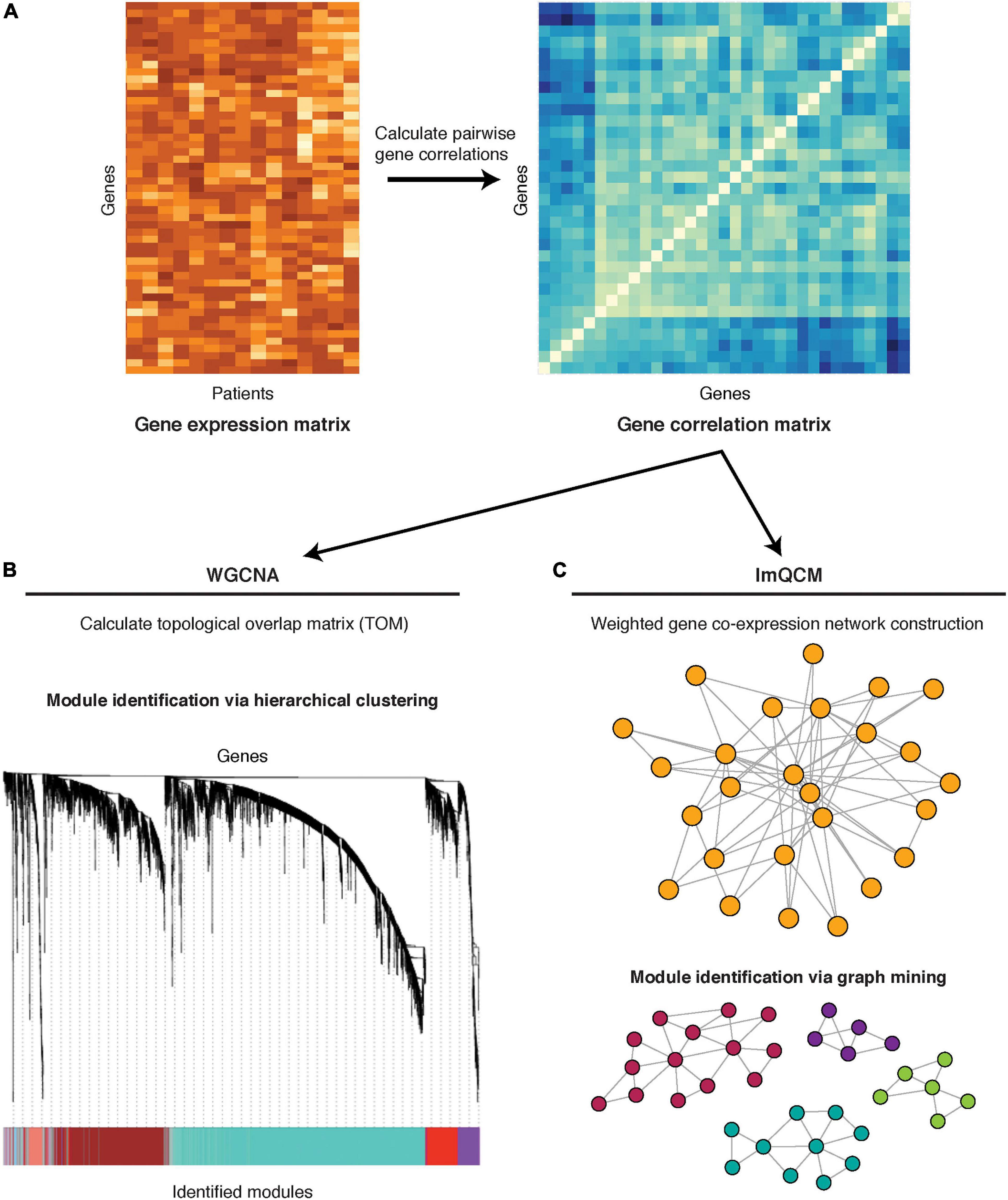
Frontiers | Mechanism-Centric Approaches for Biomarker Detection and Precision Therapeutics in Cancer






